Multimedia Learning Principles & Sketchnoting
The following video by Dr. Ray Pastore provides a brief summary of the main components of which Mayer’s cognitive theory of multimedia learning is built upon such as dual coding (the two channel structure of audio and visual material), cognitive load (the limited processing capacity in memory), and the three types of memory stores (sensory, working and long-term).
Dr. Pastore also explores several key multimedia learning design principles, which when followed, may aid in reducing extraneous processing, managing essential processing and/or fostering generative processing.
After reflecting on his video, I found that Dr. Pastore did not follow three multimedia learning principles:
- Redundancy principle – this principle focuses on the idea that “people learn better when the same information is not presented in one or more format” (Mayer 2014). Throughout the video, Dr. Pastore verbally repeated the same bullets of information that were already presented on the screen behind him.
- Modality principle – this principle states that “people learn better from graphics and narration than from graphics and printed text” (Mayer 2014). When introducing a multimedia principle, Dr. Pastore utilized text underneath his graphics to explain his diagrams.
- Embodiment principle – this principle posits that “people do not necessarily learn better when the speaker’s image is on the screen” (Mayer 2014). Dr. Pastore included a visual recording of himself as he spoke on the bottom corner of the video.
Although it may appear odd that an expert, such as Dr. Pastore, was unable to follow all of the multimedia learning principles, it is essentially impossible to adhere to every one as some principles are inherently contradictory of each other. For example, in attempting to support the redundancy principle, you may be working against the multiple representation principle, which states that “there are circumstances under which people learn better from multiple representations” (Mayer 2014). Ultimately, when designing a multimedia learning object, it is important to keep in mind the needs and preferences of your own individual students when striving to incorporate best practices.
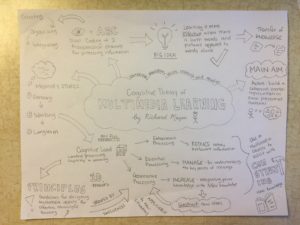
Below I have included an image of a sketchnote I have made to illustrate my understanding of multimedia learning theory.
H5P – An Interactive Digital Application
The H5P tool is a free, online tool for creating interactive HTML content. I believe that a thoughtfully created H5P interactive video would support a large majority of Mayer’s multimedia learning principles.
In particular, I think that the utilization of the captioning function for highlighting key information as well as the integration of multiple choice questions throughout the video would effectively demonstrate both the feedback principle and the signalling principle. I can also see how the segmenting principle may be followed as the option to pause, rewind and re-watch certain parts of the video allows students to take control of their learning and determine the pace in which they absorb the multimedia message.
Overall, I am very excited to incorporate H5P into my teaching practice. I think it is a wonderful tool that is easily customizable for different grade levels. For younger learners, I would focus on using captioning or animations to emphasize key points. Older learners who are working through more sophisticated material would benefit from multiple choice questions which provide immediate feedback.
Below I have included an example of an interactive H5P video on Media Literacy which I created during the class lab.
References
Mayer, R. (2014). Introduction to Multimedia Learning. In R. Mayer (Ed.), The Cambridge Handbook of Multimedia Learning (Cambridge Handbooks in Psychology, pp. 1-24). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. DOI:10.1017/CBO9781139547369.002
Ray Pastore, Phd. (2018, August 16). What is multimedia learning? What is multimedia? [Video]. Youtube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g-sknUVq1mk&feature=emb_title






Comments by leona